Understanding the early signs and detection of liver cancer
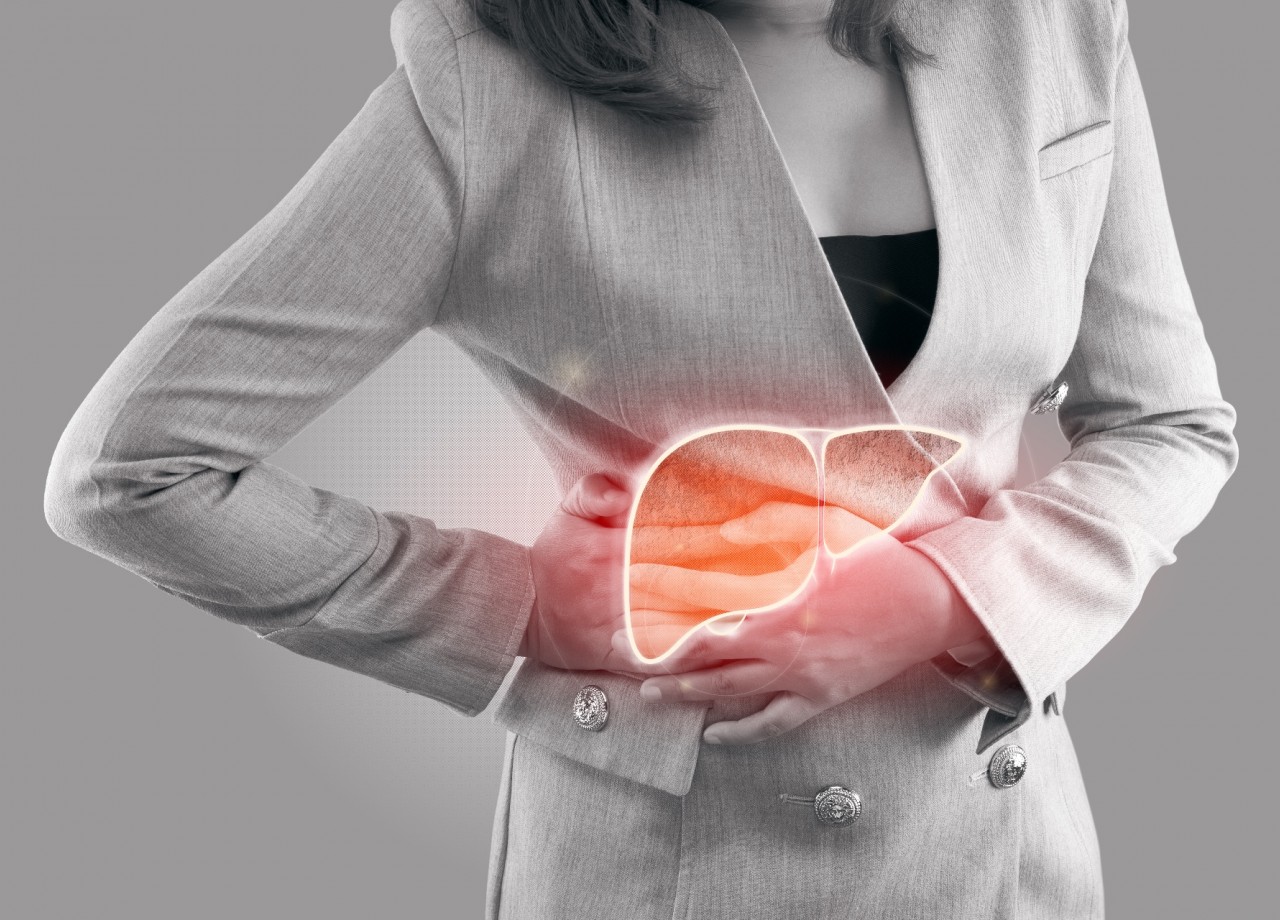
Liver cancer is a severe disease that begins in the cells of the liver, an organ located in the upper right portion of the abdomen. The liver performs numerous vital functions, including detoxifying harmful substances in the body, storing vitamins and nutrients, producing bile to aid digestion, and making proteins that help blood clot. Two main types of liver cancer include hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma, also known as bile duct cancer.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing liver cancer. These include chronic infection with hepatitis B or C virus, cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), certain inherited liver diseases, diabetes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, exposure to aflatoxins (poisons produced by molds that grow on crops stored in damp conditions), and excessive alcohol consumption.
Signs and Symptoms
Liver cancer in its early stages may not present any symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may start to appear. These include:
- Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss
- Feeling very full after a small meal (early satiety)
- Nausea or vomiting
- An enlarged liver, felt as a mass under the ribs on the right side
- An enlarged spleen, felt as a mass under the ribs on the left side
- Pain in the abdomen or near the right shoulder blade
- Swelling or fluid build-up in the abdomen (ascites)
- Itching
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
It's essential to note that these symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than liver cancer. If you experience any of these symptoms and they persist, consult your healthcare provider immediately.
Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection of liver cancer can significantly improve the prognosis and potential for a cure. Here are some ways to watch out for early signs:
1. Regular Check-ups: Regular physical examinations can help detect liver cancer early, especially for individuals with known risk factors.
2. Liver Function Tests: These blood tests measure specific proteins and liver enzymes to assess the liver's health and functioning. Abnormal results may indicate liver disease and require further investigation.
3. Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT, and MRI scans can help identify any abnormalities or tumors in the liver.
4. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) Blood Test: AFP is a protein produced by the liver. Elevated levels of AFP in the blood may indicate liver cancer.
5. Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of liver tissue to examine under a microscope for cancer cells.
Liver cancer can be life-threatening, but when detected early, the prognosis can significantly improve. Individuals with risk factors for liver cancer should be vigilant about their liver health and seek regular medical screenings. However, experiencing the symptoms mentioned doesn't necessarily mean you have liver cancer, but it's essential to get any persistent symptoms checked out by a healthcare provider. They can help diagnose the problem, rule out serious conditions, and guide you towards the appropriate treatment, if necessary.
For more information, contact us at:
Phone: 0-2677-7077
Facebook: ADDLIFECenter
Line: @addlife
www.add-life.org