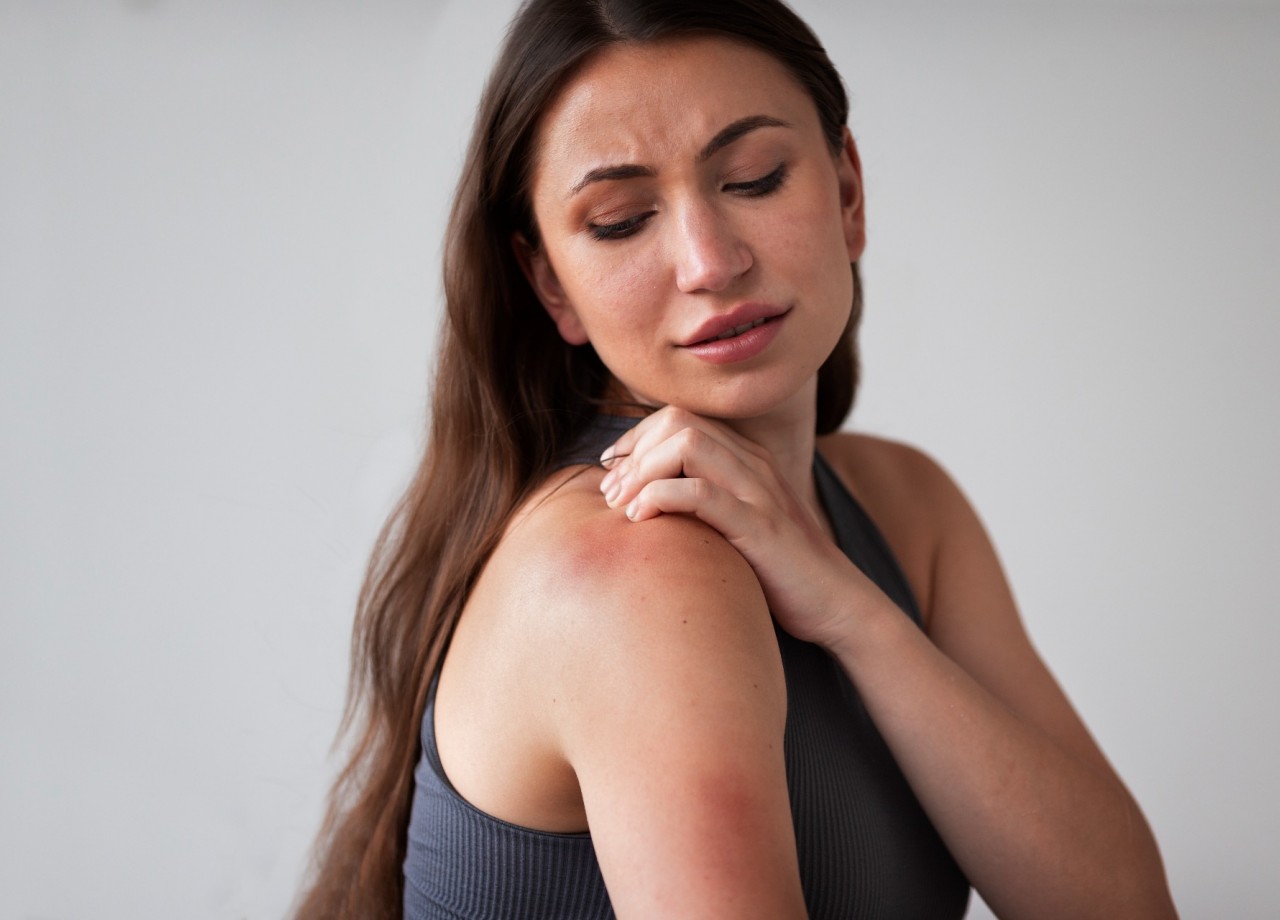
Itchy skin, rashes and eczema: causes and treatment
Skin complaints such as itchiness, rashes, and eczema are quite common and can be caused by a variety of factors. The causes can range from environmental irritants and allergies, to systemic conditions and even mental stress. In this article, we'll explore these causes in depth, including the role of latent food allergies, and look at possible treatment options.
What Causes Itchy Skin, Rashes, and Eczema?
1. Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental substances can lead to skin irritation and itchiness. These include chemicals, dyes, detergents, soaps, and fabrics. Furthermore, climatic conditions like dry, cold weather can sap moisture from the skin leading to itchiness and possible development of eczema, particularly in susceptible individuals.
2. Systemic Conditions
Itchy skin and rashes can also be caused by systemic illnesses such as liver disease, kidney disease, thyroid problems, certain cancers, and autoimmune conditions like lupus. In these situations, the itch is often generalized, and other symptoms often accompany it.
3. Neurological Causes
Some neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis, neuropathy, and shingles can cause itching. Additionally, mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression can exacerbate or even cause itchy skin and rashes, a phenomenon known as psychogenic pruritus.
4. Allergic Reactions
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that occurs as an allergic reaction to a substance like nickel, rubber, or certain cosmetic ingredients. It results in a localized rash that can be intensely itchy.
5. Latent Food Allergies
An often overlooked cause of skin problems is latent food allergies. These allergies can sometimes manifest as eczema or other skin issues like chronic itchiness or rashes. In these cases, the immune system responds to certain food proteins as if they were harmful, leading to inflammation and subsequent skin issues. Common foods linked with such reactions include dairy, eggs, nuts, soy, and gluten.
Treatment Options
The treatment of itchy skin, rashes, and eczema largely depends on the underlying cause. Treatment options include:
1. Topical Treatments
Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids are often used to reduce inflammation and itching. For eczema, there are additional treatments like calcineurin inhibitors and phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors. Moisturizing creams and lotions can help soothe dry skin and reduce itching.
2. Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can help reduce itching, especially when it's due to an allergic reaction. Some newer generation antihistamines do not cause drowsiness, a common side effect of older ones.
3. Systemic Medications
For more severe conditions, systemic medications may be required. These include oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressant drugs, or targeted biologic medications that specifically interfere with the immune responses causing the skin inflammation.
4. Elimination Diets
In the case of latent food allergies, an elimination diet may be recommended. This involves removing suspected foods from the diet for a few weeks and then gradually reintroducing them one at a time to see if symptoms reappear. If a particular food is identified as a trigger, a long-term avoidance strategy or desensitization protocols may be recommended under the guidance of an allergy specialist.
The causes of itchy skin, rashes, and eczema are numerous and varied. Finding the exact cause may take time and involve a process of elimination. Nonetheless, once the cause is identified, effective treatments are available for most conditions. As research progresses, our understanding of skin conditions and their relation to factors like food allergies continues to grow, offering hope for more targeted and effective treatments in the future. As always, consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider to identify the right treatment strategy for your individual condition.
For more information, contact us at:
Phone: 0-2677-7077
Facebook: ADDLIFECenter
Line: @addlife
www.add-life.org