How to Manage Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
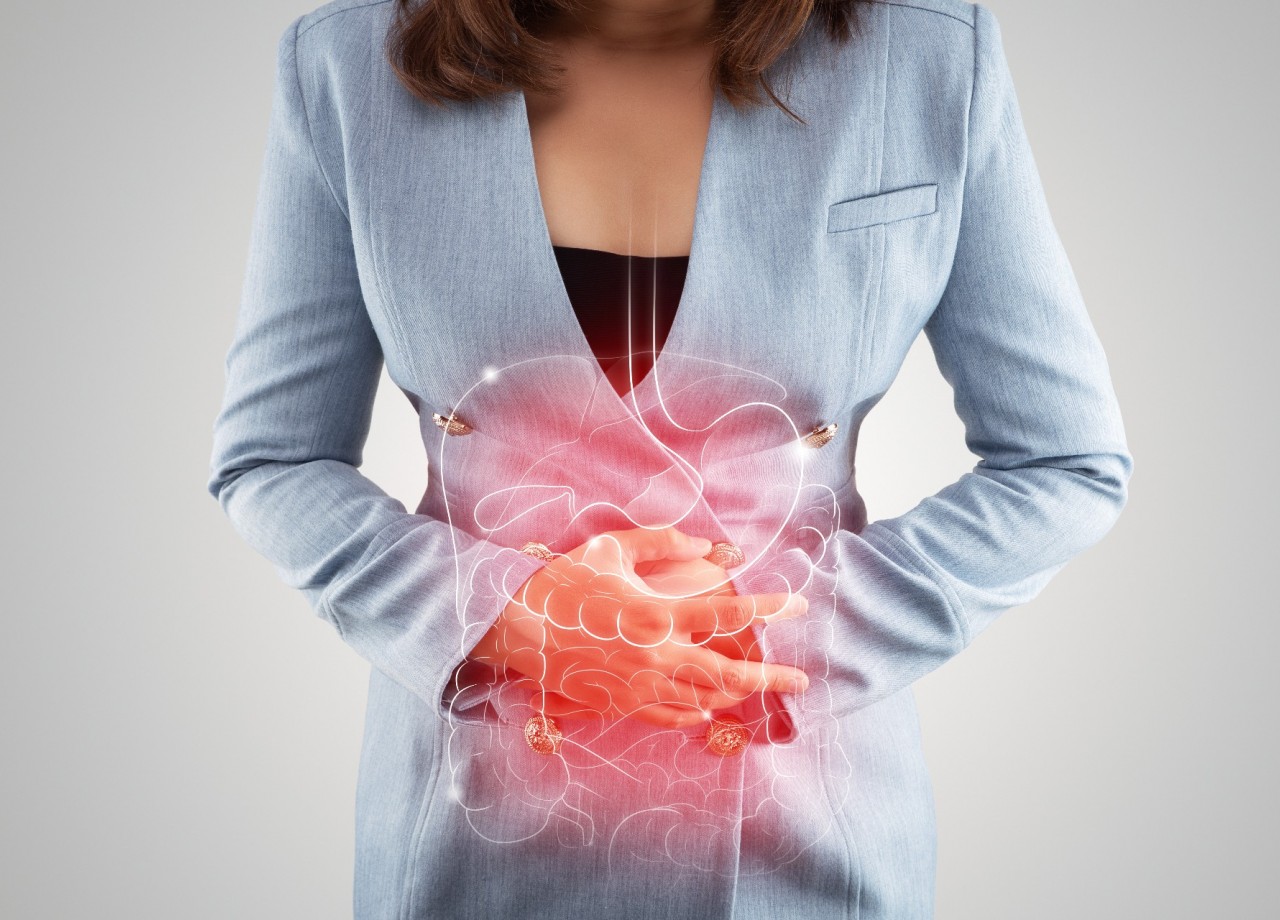
IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder that primarily affects the large intestine. While the exact cause of IBS remains unknown, it is believed to result from a combination of factors, including abnormal contractions of the intestinal muscles, increased sensitivity to pain within the gut, and disturbances in the gut-brain connection. IBS is often associated with stress, hormonal changes, and certain foods.
The symptoms of IBS can vary significantly from person to person and may be triggered or exacerbated by stress, specific foods, or hormonal changes. Common IBS symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping: The most common symptom of IBS is recurring abdominal pain or cramping, often relieved after a bowel movement.
- Bloating and gas: IBS sufferers may experience excessive gas and bloating, causing discomfort and abdominal distension.
- Changes in bowel habits: IBS can cause constipation, diarrhea, or a combination of both, often alternating between the two.
- Mucus in the stool: Some individuals with IBS may notice an increased amount of mucus in their stool.
- Urgency and incomplete bowel movements: IBS can cause an urgent need to use the restroom and a feeling of incomplete evacuation after a bowel movement.
Treatment Options for IBS
There is no one-size-fits-all cure for IBS, but a combination of dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions can help manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
- Dietary changes: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods can significantly help manage IBS symptoms. A low-FODMAP (Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols) diet may be recommended to reduce gas production and bloating. This diet involves limiting high-FODMAP foods such as onions, garlic, beans, and certain fruits, and gradually reintroducing them to identify personal triggers.
- Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, stress management techniques (e.g., meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises), and establishing a consistent sleep pattern can all contribute to improved IBS symptom management.
- Over-the-counter medications: Depending on whether IBS manifests as constipation or diarrhea, over-the-counter medications such as fiber supplements, laxatives, or anti-diarrheal medications can help manage symptoms.
- Prescription medications: In some cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe medications to manage specific IBS symptoms, such as antispasmodics to reduce abdominal cramping or low-dose antidepressants to alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Probiotics: Some IBS sufferers find relief through the use of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that promote gut health. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable probiotic strains and dosages for your needs.
IBS is a complex and often frustrating condition, but with a combination of dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve one's quality of life. If you suspect you have IBS, consult with a healthcare professional to discuss your symptoms, obtain a proper treatment plan.
Learn more about ADDLIFE’s Ultimate Gut Microbiome DNA Test
For more information, contact us at:
Phone: 0-2677-7077
Facebook: ADDLIFECenter
Line: @addlife
www.add-life.org