Understanding Telomeres and Their Impact on Aging
What Are Telomeres?
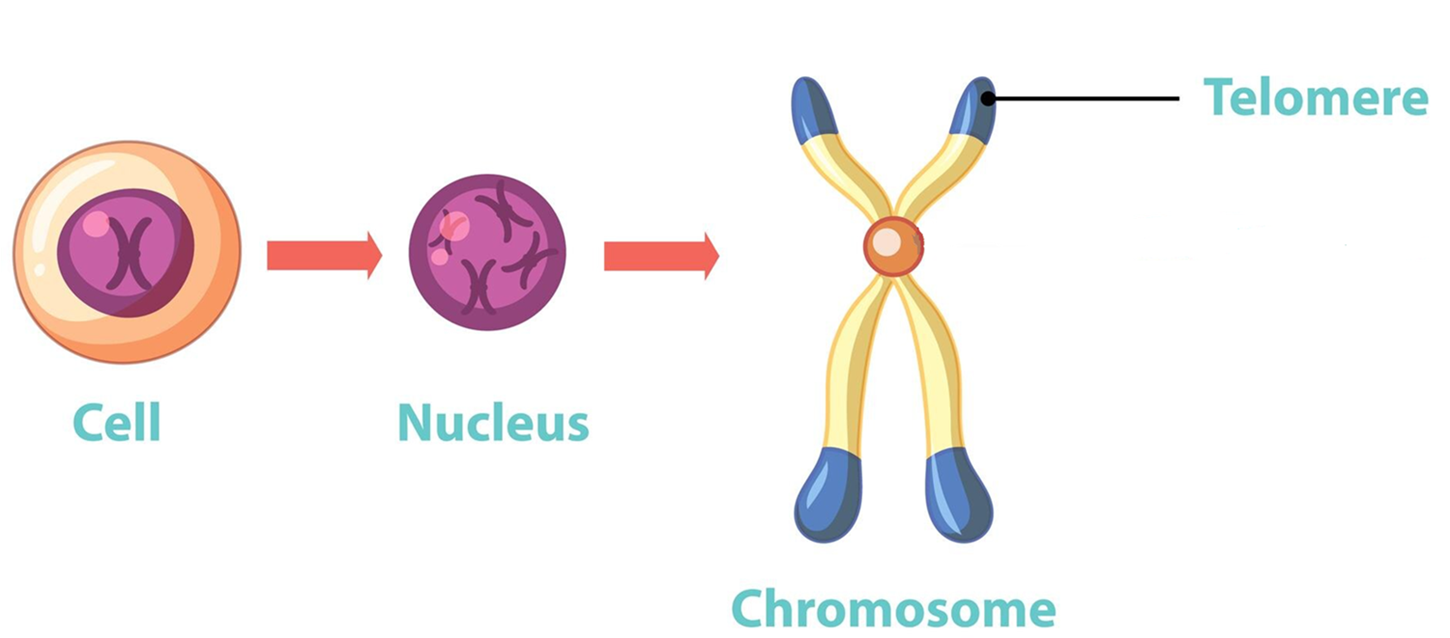
Telomeres are the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, composed of repetitive DNA sequences. They do not encode proteins but serve a crucial role in preventing chromosomes from deteriorating or fusing with each other. Every time a cell divides, telomeres shorten, which is a natural part of aging. However, environmental factors and lifestyle choices can accelerate this shortening process.
Why Measure Telomere Length?
In 2009, scientists Elizabeth H. Blackburn, Carol W. Greider, and Jack W. Szostak were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for their discovery of telomere protection mechanisms and the enzyme telomerase, which helps maintain telomere length.
Measuring telomere length can provide insights into cellular aging and potential health risks. It helps in assessing biological age, identifying disease susceptibility, and developing personalized lifestyle and medical interventions to slow down aging and cellular degeneration.
Can We Lengthen Telomeres?
Recent research has explored ways to extend telomere length using telomerase activation. While telomere shortening is inevitable, interventions may help slow down this process.
What is Telomerase?
Telomerase is an enzyme that replenishes and extends telomeres. It is active during early development and in stem cells, but in most adult cells, its activity is minimal. As a result, telomeres progressively shorten with each cell division, eventually leading to cell death (apoptosis).
Why is Telomerase Important?
Every time a cell divides, its telomeres shorten. Over time, this shortening leads to cellular aging and eventual cell death. Telomerase counteracts this process by adding repetitive DNA sequences to telomeres, effectively extending their lifespan.
How to Maintain Healthy Telomeres
Modern lifestyles contribute to telomere shortening, but adopting healthy habits can help maintain their length:
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for at least 8 hours per night and sleep before 10 PM.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink at least 8 glasses (2 liters) of water daily.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Reduce processed foods, trans fats, and excessive sugar. Focus on fiber-rich foods, lean proteins like poultry and fish, and whole grains.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in cardio activities like running, swimming, or cycling for 30 minutes, five times a week, or walk 10,000 steps daily.
- Manage Stress: Practice meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness to reduce chronic stress.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: These habits accelerate telomere shortening and increase disease risks.
Additionally, maintaining a positive mindset and emotional well-being can play a significant role in cellular health. A combination of a balanced lifestyle and preventive healthcare can slow down telomere shortening, promoting longevity and overall well-being.e.
Planning for Long-Term Health
Telomere length testing can help determine biological age and the rate of cellular aging. This knowledge allows individuals to make proactive lifestyle changes to reduce disease risks such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, Alzheimer's, and diabetes.
By avoiding harmful habits and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can preserve telomere integrity, enhance cellular function, and enjoy a longer, healthier life.