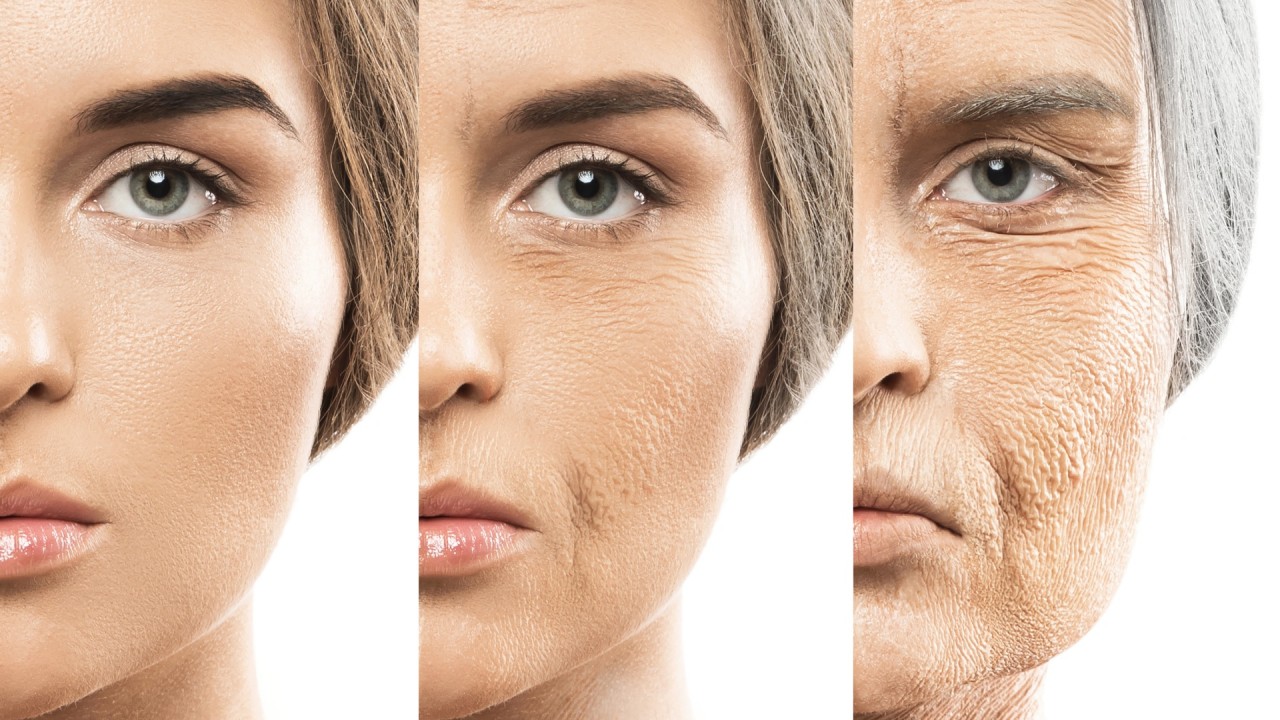
What really is Anti-Aging medicine?
Anti-aging medicine is a branch of medical science that focuses on slowing down, preventing, or reversing the aging process. It aims to prolong the healthy, active years of life by targeting the underlying causes of aging and age-related diseases. This field of medicine utilizes various approaches, including lifestyle changes, hormone therapies, cellular and genetic therapies, and nutritional supplementation, among others.
The effectiveness of anti-aging medicine varies from person to person, as individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors play significant roles in how one ages. Some anti-aging interventions, like maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, have been shown to be generally effective in promoting overall health and longevity.
In recent years, several popular anti-aging treatments have gained attention for their potential to slow down or reverse the aging process. Some of the most popular treatments include:
-
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): Hormone levels naturally decline as we age, and hormone replacement therapy aims to restore the balance of hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and human growth hormone (HGH). HRT has shown some potential in improving various age-related symptoms, but its long-term safety and effectiveness are still under debate.
-
Telomerase activators: Telomeres are the protective caps at the end of our chromosomes that shorten as our cells divide, eventually leading to cellular senescence or death. Telomerase activators, such as TA-65 and Cycloastragenol, are supplements that claim to stimulate the enzyme telomerase, potentially slowing down the shortening of telomeres and promoting cellular health. However, more research is needed to confirm their efficacy and safety.
-
Caloric restriction and intermittent fasting: Both caloric restriction and intermittent fasting have been shown to extend the lifespan of various organisms, including yeast, worms, and mice, by triggering cellular repair and maintenance processes. Some studies have suggested that these dietary interventions may also provide anti-aging benefits in humans, but more research is needed to confirm their long-term safety and effectiveness.
-
Antioxidants and supplements: Antioxidants such as resveratrol, coenzyme Q10, and vitamins C and E are popular anti-aging supplements that claim to combat the damaging effects of free radicals and oxidative stress, which contribute to the aging process. Although some studies have shown promising results, the overall effectiveness of these supplements remains uncertain.
-
Senolytics: These are a class of drugs that selectively target and eliminate senescent cells – cells that have stopped dividing and contribute to aging and age-related diseases. Senolytics, such as Dasatinib and Quercetin, are still in the experimental stage, and their long-term safety and effectiveness require further investigation.
-
Aesthetic treatments: Cosmetic procedures such as Botox, dermal fillers, chemical peels, and laser treatments are widely used to reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. While these treatments mostly address the visible signs of aging, they do not target the underlying biological processes that cause aging.
Anti-aging medicine is a proactive approach focused on enhancing health and vitality as we age. By combining personalized nutrition, hormone balance, advanced screenings, and lifestyle adjustments, it aims to prevent age-related issues and improve quality of life. This field empowers individuals to live healthier, fuller lives at every stage through science-driven practices.